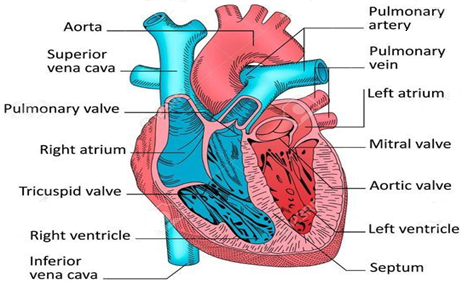
Artery ও Vein মূলত রক্তনালি। যেসব রক্তনালির মাধ্যমে অক্সিজেনসমৃদ্ধ রক্ত হৃৎপিণ্ড থেকে সারা দেহে বাহিত হয়, তা-ই Artery। যেসব নালি দিয়ে রক্ত দেহের বিভিন্ন অংশ থেকে হৃৎপিণ্ডে ফিরে আসে তাদের Vein বলে। নিচে ধমনি ও শিরার মধ্যে পার্থক্য তুলো ধরা হলো
যেসব নালি দিয়ে রক্ত দেহের বিভিন্ন অংশ থেকে হৃৎপিণ্ডে ফিরে আসে, তাদের শিরা বলে। শিরা কার্বন ডাই-অক্সাইডসমৃদ্ধ রক্ত পরিবহন করে হৃৎপিণ্ডে নিয়ে আসে। ফুসফুসীয় শিরা বা পালমোনারি শিরা অক্সিজেনসমৃদ্ধ রক্ত ফুসফুস থেকে হৃৎপিণ্ডে পৌঁছে দেয়। এ জন্য ফুসফুসীয় শিরাকে ব্যতিক্রমধর্মী শিরা বলা হয়।
মানুষের হৃৎপিণ্ডের মধ্যে দিয়ে রক্ত সংবহন (Blood circulation through human heart):
মানব দেহের হৃৎপিণ্ড একটি ছন্দে সংকোচিত ও প্রসারিত হয়ে সংবহন তন্ত্রের রক্তকে সচল রাখে । হৃৎপিণ্ডের সংকোচনকে সিস্টোল ও প্রসারন কে ডায়াস্টোল বলে । হৃৎপিণ্ডের একটি সিস্টোল ও ডায়াস্টোল কে এক সঙ্গে একটি হৃৎস্পন্দন বলে । হৃৎপিণ্ডের রক্ত সঞ্চালন প্রক্রিয়াটি নিম্নলিখিত কতগুলি কার্যে বিভক্ত -
১৷ অলিন্দদ্বয় (Atrium) প্রসারিত হলে সারা শরীরের দুষিত রক্ত ঊর্ধ্ব ও মহাশিরা দিয়ে ডান অলিন্দে (Right Atrium) আসে । একি সময় ফুসফুস থেকে বিশুদ্ধ রক্ত ফুসফুসীয় শিরা দিয়ে বাম অলিন্দ (Left Atrium) আসে ।
২৷ অলিন্দদ্বয় (Atrium) রক্তে পূর্ণ হলে সংকুচিত হয় এবং নিলয়দ্বয় (Ventricle) প্রসারিত হয় । তখন ডান অলিন্দের রক্ত ত্রিপত্র কপাটিকার ভিতর দয়ে ডান নিলয়ে আসে এবং বাম অলিন্দের রক্ত দ্বিপত্র কপাটিকার ভিতর দিয়ে বাম নিলয়ে প্রবেশ করে ।
৩৷ নিলয়দ্বয় (Ventricle) সম্পূর্ণ রক্তে পূর্ণ হলে সংকোচিত হয় এবং ডান নিলয় থেকে ফুসফুসীয় ধমনীর মাধ্যমে ফুসফুসে প্রবেশ করে । বাম নিলয় থেকে মহা ধমনীর মাধ্যমে সারা দেহে ছড়িয়ে পড়ে । এই সময় অর্ধচন্দ্রাকৃতি কপাটিকা খুলে যায় এবং দ্বিপত্র ও ত্রিপত্র কপাটিকা বন্ধ থাকে ।
৪৷ এর পর আবার অলিন্দ দ্বয় প্রসারিত হলে রক্ত অলিন্দে প্রবেশ করে । এইভাবে সংকোচন ও প্রসারনের মাধ্যমে রক্ত সঞ্চালনের পদ্ধতিটি অব্যহত থাকে ।
 |
| Blood Flow |
হৃৎপিণ্ডের গঠন (Structure of Human Heart):
মানুষের হৃৎপিণ্ডটি বক্ষ গহ্বরে ফুসফুস দ্বয়ের মাঝখানে ও মধ্যছদার উপরে অবস্থিত। ইহা ত্রিকোণাকার পেশী বহুল সক্রিয় যন্ত্র বিশেষ । মানব দেহের হৃৎপিণ্ডটি লম্বালম্বি ছেদ করলে নিম্নলিখিত অংশ গুলি দেখা যায়-
১৷ প্রকোষ্ঠ (Closet)
মানুষের হৃৎপিণ্ডে প্রকোষ্ঠের সংখ্যা চারটি যথা- ক) ডান অলিন্দ, খ) ডান নিলয়, গ) বাম অলিন্দ, ঘ) বাম নিলয়
অলিন্দ (Atrium)- ইহা হৃৎপিণ্ডের সংগ্রাহক প্রকোষ্ঠ । অলিন্দের সংখ্যা দুটি- যথা- ডান অলিন্দ, বাম অলিন্দ। উভয় অলিন্দ অন্ত অলিন্দ প্রাচীর দ্বারা বিভেদিত ।
ক) ডান অলিন্দ (Right Atrium) - ডান অলিন্দে ঊর্ধ্ব মহাশিরা ও নিম্ন মহাশিরা যুক্ত থাকে । ইহার মাধ্যমে দুষিত রক্ত ডান অলিন্দে প্রবেশ করে । ডান অলিন্দের প্রাচীরে অবস্থিত স্পেস মেকার হৃৎপিণ্ডের ছন্দ গতিকে নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে ।
খ) বাম অলিন্দ (Left Atrium) - এই অলিন্দে চারটি ফুসফুসীয় শিরা যুক্ত থাকে । এর মাধ্যমে বিশুদ্ধ রক্ত বাম অলিন্দে প্রবেশ করে ।
নিলয় (Ventricle) - ইহা হৃৎপিণ্ডের প্রেরক প্রকোষ্ঠ। ইহার অন্তঃ প্রাচীর পেশী বহুল খাঁজ যুক্ত । এই খাঁজ গুলিকে কলামনি কারনি বলে। নিলয় দুটি পরস্পর আন্ত নিলয় প্রাচীর দ্বারা বিভেদিত ।
গ) ডান নিলয় (Right Ventricle) - ইহার সাথে ফুসফুসীয় ধমনী যুক্ত থাকে । এর মাধ্যমে কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইড যুক্ত দুষিত রক্ত ফুসফুসে প্রবেশ করে।
ঘ) বাম নিলয় (Left Ventricle) - ইহার সাথে যুক্ত থাকে মহা ধমনী, যার মাধ্যমে অক্সিজেন পূর্ণ বিশুদ্ধ রক্ত সজীব কোষে পৌঁছায় ।
Artery _ ধমনি
- উৎপত্তিস্থল হৃৎপিণ্ড।
- রক্তের গতির দিক সাধারণত হৃৎপিণ্ড থেকে দেহের বিভিন্ন দিকে।
- অক্সিজেন বেশি থাকে বলে রক্ত টাটকা লাল।
- নাড়ি স্পন্দন আছে।
- প্রাচীরের মধ্যস্তর পেশিবহুল ও পুরু।
Vein _ শিরা
- উৎপত্তিস্থল কৈশিক জালিকা।
- রক্তের গতির দিক সাধারণত দেহের বিভিন্ন দিক থেকে হৃৎপিণ্ডের দিকে।
- কার্বন ডাই-অক্সাইড বেশি থাকে বলে কালচে লাল বা নীল রঙের।
- নাড়ি স্পন্দন নেই।
- প্রাচীরের মধ্যস্তর অল্প পেশিযুক্ত ও পাতলা।
কপাটিকা (Valve):
কপাটিকার নামঃ
- ট্রাইকাসপিড বা ত্রিপক কপাটিকা
- বাইকাস পিড বা মাইট্রাল বা দ্বিপত্র কপাটিকা
- পালমনারি কপাটিকা
- অ্যাওটিক কপাটিকা
অবস্থানঃ
- ডান অলিন্দ ও ডান নিলয়ের সংযোগস্থলে অবস্থিত ।
- বাম অলিন্দ ও বাম নিলয়ের সংযোগস্থলে অবস্থিত ।
- ডান নিলয় ও ফুসফুসীয় ধমনীর সংযোগস্থলে অবস্থিত ।
- বাম নিলয় ও মহা ধমনীর সংযোগস্থলে অবস্থিত ।
কাজঃ
- ডান অলিন্দ থেকে রক্তকে ডান নিলয়ে প্রেরন করা কিন্তু রক্তকে বিপরীত পথে যেতে বাধা দেওয়া।
- বাম অলিন্দ থেকে রক্তকে বাম নিলয়ে প্রেরন করা কিন্তু রক্তকে বিপরীত পথে যেতে বাধা দেওয়া।
- রক্তকে ডান নিলয় থেকে ফুসফুসীয় ধমনীতে প্রেরন করা, কিন্তু রক্তকে বিপরীত পথে যেতে বাধা দেওয়া।
- রক্তকে বাম নিলয় থেকে মহা ধমনীতে প্রেরন করা, কিন্তু রক্তকে বিপরীত পথে যেতে বাধা দেওয়া।
 |
| Cardiovascular System |
Functions of the Heart:
- Managing blood supply. Variations in the rate and force of heart contraction match blood flow to the changing metabolic needs of the tissues during rest, exercise, and changes in body position.
- Producing blood pressure. Contractions of the heart produce blood pressure, which is needed for blood flow through the blood vessels.
- Securing one-way blood flow. The valves of the heart secure a one-way blood flow through the heart and blood vessels.
- Transmitting blood. The heart separates the pulmonary and systemic circulations, which ensures the flow of oxygenated blood to tissues.
Anatomy of the Heart
 |
| Anatomy of the Heart |
Heart Structure and Functions
- Our heart is composed almost entirely of a muscle layer called myocardium. the heart beings beating 18 days after conception and stops only when you die.
- An adult's heart beats an average 72x a minute, pumping about 70 milliliters (about 2.5 cups) of blood with each contraction.
Layers of the Heart
The heart muscle has three layers and they are as follows:
- Epicardium. The epicardium or the visceral and outermost layer is actually a part of the heart wall.
- Myocardium. The myocardium consists of thick bundles of cardiac muscle twisted and whirled into ringlike arrangements and it is the layer that actually contracts.
- Endocardium. The endocardium is the innermost layer of the heart and is a thin, glistening sheet of endothelium hat lines the heart chambers.

Layers of the Heart
Chambers of the Heart
The heart has four hollow chambers, or cavities: two atria and two ventricles.
- Receiving chambers. The two superior atria are primarily the receiving chambers, they play a lighter role in the pumping activity of the heart.
- Discharging chambers. The two inferior, thick-walled ventricles are the discharging chambers, or actual pumps of the heart wherein when they contract, blood is propelled out of the heart and into the circulation.
- Septum. The septum that divides the heart longitudinally is referred to as either the interventricular septum or the interatrial septum, depending on which chamber it separates.

Chambers of the Heart
Associated Great Vessels
The great blood vessels provide a pathway for the entire cardiac circulation to proceed.
- Superior and inferior vena cava. The heart receives relatively oxygen-poor blood from the veins of the body through the large superior and inferior vena cava and pumps it through the pulmonary trunk.
- Pulmonary arteries. The pulmonary trunk splits into the right and left pulmonary arteries, which carry blood to the lungs, where oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide is unloaded.
- Pulmonary veins. Oxygen-rich blood drains from the lungs and is returned to the left side of the heart through the four pulmonary veins.
- Aorta. Blood returned to the left side of the heart is pumped out of the heart into the aorta from which the systemic arteries branch to supply essentially all body tissues.
Heart Valves:
The heart is equipped with four valves, which allow blood to flow in only one direction through the heart chambers.
 |
| Heart Valves |
Cardiac Circulation Vessels:
Although the heart chambers are bathed with blood almost continuously, the blood contained in the heart does not nourish the myocardium.
- Coronary arteries. The coronary arteries branch from the base of the aorta and encircle the heart in the coronary sulcus (atrioventricular groove) at the junction of the atria and ventricles, and these arteries are compressed when the ventricles are contracting and fill when the heart is relaxed.
- Cardiac veins. The myocardium is drained by several cardiac veins, which empty into an enlarged vessel on the posterior of the heart called the coronary sinus.
Cardiovascular System
- Hypertension
- Hypertensive Heart Disease
- Atherosclerosis
- Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
- Myocardial Infarction (MI)
- Cardiac Hypertrophy
- Heart Valve Diseases
What is Hypertension?
High blood pressure (HBP or hypertension/ HTN) is when the force of blood pushing against the walls of the blood vessels, is consistently too high.
Persistent rise of systemic blood pressure above normal upper level.
High blood pressure (HBP or hypertension/ HTN) is when the force of blood pushing against the walls of the blood vessels, is consistently too high.
Persistent rise of systemic blood pressure above normal upper level.
 |
| Hypertension |
There are two types of hypertension:
- Primary: High blood pressure that is not related to another medical condition.
-90% to 95% of all cases
- Secondary: Another medical condition that causes high blood pressure, usually occurring in the kidneys, arteries, heart, or endocrine system.
-5% to 10% in adults
The common complications are target organ diseases occurring in the Heart, Brain, Kidney and Eyes.
Systemic Hypertension is the persistent high blood pressure in the systemic arteries.
High systemic blood pressure is usually caused by the constriction of the small arteries or arterioles.
Systemic Hypertension is the persistent high blood pressure in the systemic arteries.
High systemic blood pressure is usually caused by the constriction of the small arteries or arterioles.
- Normal systolic blood pressure: Up to 140 mm Hg
- Normal diastolic blood pressure: Up to 90 mm Hg
Increases for Hypertension and High blood pressure:
Risk of strokes
Heart attacks (myocardial infarction)
Atherosclerosis
Kidney failure
Cerebral hemorrhage
Hypertensive Heart Disease
Coronary artery disease
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Heart failure
Cerebrovascular Disease
Stroke
Peripheral Vascular Disease
Nephro-sclerosis
Retinal Damage
Atherosclerosis is a disease in which plaque builds up inside arteries; also known as Arteriosclerosis
অ্যাথেরোস্ক্লেরোসিস এমন একটি রোগ যা প্লাকটি ধমনীর ভিতরে তৈরি করে; আর্টেরিওস্ক্লেরোসিস নামেও পরিচিত
Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. Over time, plaque hardens and narrows arteries. This limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood to organs and other parts of body which provoke chronic inflammation, ultimately causing thrombosis or stenosis.
প্ল্যাকুই: ফলক ফ্যাট, কোলেস্টেরল, ক্যালসিয়াম এবং রক্তে পাওয়া অন্যান্য পদার্থ নিয়ে গঠিত। সময়ের সাথে সাথে ফলক শক্ত হয়ে যায় এবং ধমনীগুলি সঙ্কুচিত করে। এটি অক্সিজেন সমৃদ্ধ রক্তের প্রবাহকে অঙ্গ এবং দেহের অন্যান্য অংশগুলিতে সীমাবদ্ধ করে যা শেষ পর্যন্ত থ্রোম্বোসিস বা স্টেনোসিস সৃষ্টি করে ।
Result of Smoking
Risk of strokes
Heart attacks (myocardial infarction)
Atherosclerosis
Kidney failure
Cerebral hemorrhage
What is the main cause of hypertension?Common factors that can lead to high blood pressure include: A diet high in salt, fat, and/or cholesterol. Chronic conditions such as kidney and hormone problems, diabetes, and high cholesterol. Family history, especially if your parents or other close relatives have high blood pressure.
Hypertensive Heart Disease
Coronary artery disease
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Heart failure
Cerebrovascular Disease
Stroke
Peripheral Vascular Disease
Nephro-sclerosis
Retinal Damage
Atherosclerosis is a disease in which plaque builds up inside arteries; also known as Arteriosclerosis
অ্যাথেরোস্ক্লেরোসিস এমন একটি রোগ যা প্লাকটি ধমনীর ভিতরে তৈরি করে; আর্টেরিওস্ক্লেরোসিস নামেও পরিচিত
Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. Over time, plaque hardens and narrows arteries. This limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood to organs and other parts of body which provoke chronic inflammation, ultimately causing thrombosis or stenosis.
প্ল্যাকুই: ফলক ফ্যাট, কোলেস্টেরল, ক্যালসিয়াম এবং রক্তে পাওয়া অন্যান্য পদার্থ নিয়ে গঠিত। সময়ের সাথে সাথে ফলক শক্ত হয়ে যায় এবং ধমনীগুলি সঙ্কুচিত করে। এটি অক্সিজেন সমৃদ্ধ রক্তের প্রবাহকে অঙ্গ এবং দেহের অন্যান্য অংশগুলিতে সীমাবদ্ধ করে যা শেষ পর্যন্ত থ্রোম্বোসিস বা স্টেনোসিস সৃষ্টি করে ।
Result of Smoking
- Increased Triglyceride and cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
Also known as Coronary Artery Disease, Ischemic Heart Disease,
When the arteries of the heart cannot deliver enough oxygenated blood to the heart.
Women are less likely than men to experience chest pain. Instead, they are more likely to experience:
Dizziness
Fatigue
Nausea
Pressure or tightness in the chest
Stomach pain
An acute coronary occasion may cause the following symptoms:
Angina
Cold sweats
Dizziness
Light-headedness
Nausea or a feeling of indigestion
Neck pain
Shortness of breath, especially with activity
Sleep disturbances
Weakness
In Chronic (long-term) coronary heart disease:
Angina (Less severe)
Shortness of breath with physical activity
Fatigue
Neck pain
Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack):When the flow of oxygen-rich blood to a section of heart muscle suddenly becomes blocked and the heart can’t get enough oxygen resulting death of heart muscle, which is clinically known as Heart Attack.
Variation of Troponin level differentiate between a injured and non-injured cardiac tissue.
Normal Range:between 0 and 0.4 ng/mL.
Pressure or tightness in the chest pain in the chest, back, jaw, and other areas of the upper body that lasts more than a few minutes or that goes away and Comes back.
Sweating
Nausea
Vomiting
Anxiety
Cough
Dizziness
Fast heart rate
In Women:
Shortness of breath
Jaw pain
Upper back pain
Lightheadedness
Nausea
Vomiting
Cardiac hypertrophy is the abnormal enlargement, or thickening, of the heart muscle, resulting from increases in cardiomyocyte size and changes in other heart muscle components, such as extracellular matrix.
কার্ডিয়াক হাইপারট্রোফি হৃৎপিণ্ডের অস্বাভাবিক বৃদ্ধি বা ঘন হওয়া, এর ফলে কার্ডিওমায়োসাইটের আকার বৃদ্ধি পায় এবং হৃৎপিণ্ডের অন্যান্য পেশীগুলির উপাদান যেমন বহির্মুখী ম্যাট্রিক্সের পরিবর্তন ঘটে।
Valvular Heart Disease:ভালভুলার হৃদরোগ
Valvular heart disease is characterized by damage to or a defect in one of the four heart valves: the mitral, aortic, tricuspid or pulmonary.
ভালভুলার হৃদরোগের চারটি হার্টের ভালভের একটিতে ক্ষতি বা একটি ত্রুটি দ্বারা চিহ্নিত করা হয়: মিট্রাল, অর্টিক, ট্রাইকস্পিড বা পালমোনারি।
The mitral and aortic valves are the ones most frequently affected by valvular heart disease.
সংবহনতন্ত্রঃ
- রক্ত সংবহনতন্ত্রঃ রক্ত,হৃৎপিন্ড,রক্তবাহিকা(শিরা,জালিকা,ধমনী)।
- লসিকা সংবহনতন্ত্রঃ লসিকা,লসিকানালী,লসিকাগ্রন্থি।
রক্তঃ ভ্রুণীয় মেসোডার্ম থেকে উৎপন্ন,লালবর্ণ,অস্বচ্ছ,লবনাক্ত,সামান্য ক্ষারধর্মী যে বিশেষ তরল যোজক কলা রক্তরস ও রক্তকণিকার সমন্বয়ে গঠিত।
- দেহে রক্তের পরিমান ৫-৬লিটার,মোট ওজনের ৮%।
- ph ৭.৩৫-৭.৪৫,তাপমাত্রা ৩৬-৩৭ ডিগ্রি সেলসিয়াস,আপেক্ষিক গুরুত্ব পানির চেয়ে বেশি-১.০৬৫।
- রক্তরসের গ্যাসীয় পদার্থ(O2,CO2,N2)
- রেচন পদার্থ/নাইট্রোজেনযুক্ত অপ্রোটিন দ্রব্য: অ্যামিনো এসিড,ইউরিয়া, ইউরিক এসিড,ক্রিয়েটিনিন।
- রক্তের প্রোটিন/প্লাজমা প্রোটিন ৪টা: অ্যালবুমিন,গ্লোবিউলিন, প্রোথ্রোম্বিন,ফাইব্রিনোজেন।
- স্নেহদ্রব্য: কোলেস্টেরল, ফসফোলিপিড,লেসিথিন।
- রঞ্জক পদার্থ: বিলিরুবিন,বিলিভারডিন।
♦রক্তের কাজঃসবগুলো পড়তে হবে।
♦রক্ত→রক্তরস/প্লাজমা(৫৫%)
↓
রক্তকণিকা/করপাসল(৪৫%)
♦রক্তরস/প্লাজমা→পানি(৯০-৯২%)+কঠিন পদার্থ(৮-১০%)
♦রক্তকণিকা/করপাসল→লোহিত রক্তকণিকা,শ্বেত রক্তকণিকা,অণুচক্রিকা।
♦♦লোহিত রক্তকণিকাঃErythrocyte→erythro=লাল+cyte=কোষ।সংক্ষিপ্ত RBC.
→গোলাকার,দ্বিঅবতল,নিউক্লিয়াসহীন,চাকতির মত।
→ভ্রুণ দেহে:৮০-৯০ লাখ।
শিশু দেহে:৬০-৭০ লাখ।
পুরুষ দেহে:৫০ লাখ।
নারী দেহে:৪৫ লাখ।
→৬০-৭০% পানি,৩০% কঠিনপদার্থ(৯০% হিমোগ্লোবিন+১০% অন্যান্য)।
→লোহিত কণিকার সংখ্যা ৫০ লাখের চেয়ে ২৫%কম হলে রক্তস্বপ্লতা(anaenia)হয়।
→৬৫ লাখের বেশি হলে পলিসাইথেমিয়া বলে।
→হিমোগ্লোবিন =হিমাটিন(অপ্রোটিন)+গ্লোবিন(প্রোটিন)।হিম লৌহ রঞ্জক,রক্ত লাল করে।
→অস্থিমজ্জায়
অবস্থিত stem cell থেকে উৎপত্তি,জীবনকাল ১২০দিন/৪মাস,১২০দিন পর প্লীহায় নষ্ট হয়।
→লোহিত রক্তকণিকাঃশ্বেত রক্তকণিকা=৭০০ঃ১।
ব্যাতিক্রম:উট,রুইমাছ,ব্যাঙ এর রক্তের লোহিত কণিকা নিউক্লিয়াসযুক্ত।
→লোহিত রক্তকণিকার কাজ।
♦♦শ্বেত রক্তকণিকাঃLeucocyte→leucos=বর্ণহীন+cyte=কোষ।সংক্ষিপ্ত WBC.
→হিমোগ্লোবিনবিহীন,অনিয়তাকার, নিউক্লিয়াসযুক্ত,বড় ফ্যাগোসাইটিক কোষ।
→গোলাকার, ডিম্বাকার, বৃক্কাকার,অশ্বক্ষুরাকার।
→পরিমাণ ৫-৮হাজার।শিশু ও অসুস্থ দেহে বেড়ে যায়।
→প্রকারভেদ:ছক(pic)
→অদানাদার=লিমা(লিম্ফোসাইট,মনোসাইট)
→দানাদার=নিইওবে(নিউট্রোফিল,ইওসিনোফিল,বেসোফিল)
→দানাদার ও অদানাদার পাথর্ক্য।
→ইওসিনোফিল রক্তে কৃমির লার্ভা,অ্যালার্জিক অ্যান্টিবডি ধ্বংস করে।
→লিম্ফোসাইট প্রদাহ অঞ্চলে ফাইব্রোব্লাস্টে পরিণত হয়ে ক্ষত নিরাময় করে।
→দানাদার লিউকোসাইট→হিস্টামিন সৃষ্টি→রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা বৃদ্ধি।
→লিম্ফোসাইট→আণুবীক্ষণিক সৈনিক।
♦♦অনুচক্রিকাঃThrombocyte/Platelets
→বর্ণহীন,নিউক্লিয়াসহীন,নির্দিষ্ট আকারহীন, ক্ষুদ্রতম কণিকা।
→পরিমাণ:২.৫-৫ লাখ।
→অস্থিমজ্জার মেগাক্যারিওসাইট থেকে উৎপত্তি।
→প্রোটিন+প্রচুর সেফালিন(ফসফোলিপিড) থাকে।
→প্লীহা,রেটিকুলো এন্ড্রোথেলিয়া কোষ এ নষ্ট হয়।
→জীবনকাল:৫-১০দিন।
→অনুচক্রিকার কাজ।
♦♦রক্ত তঞ্চন/রক্ত জমাট বাধা(Blood Clotting):
♦Clotting factors:13টা।নাম গুলো মনে রাখলেই হবে।তবে অত্যাবশ্যকীয় ৪টা।
ফসহজ ভাবে তোমাদের জন্য দিচ্ছি →
১.ক্ষতস্থানের কোষ+থ্রম্বোসাইট+বাতাস(হেপারিন অকেজো)→থ্রম্বোপ্লাস্টিন(one type of anzyme)
২.থ্রম্বোপ্লাস্টিন+(Ca++)+প্রোথ্রোম্বিন+অন্যান্য বস্তু→থ্রম্বিন(one type of anzyme)
৩.থ্রম্বিন+ফাইব্রিনোজেন →ফাইব্রিন জালক।
৪.ফাইব্রিন জালকে লোহিত কণিকাসমূহ আবদ্ধ→রক্ত জমাট বাধা।
→Bleeding time:1-4minute.
→Clotting time:4-5minute.
→রক্ত তঞ্চন রোধক পদার্থ:সোডিয়াম সাইট্রেট,ব্লাড ব্যাংক এ ব্যাবহার হয়।
→রক্তকণিকা সৃষ্টির প্রক্রিয়াকে 'হেমাটোপোয়েসিস' বলে।
আমরা জানি,আমাদের শরীর এর একটা গুরুত্বপূর্ণ একটা অংশ Heart-হৃদপিন্ড
রক্তবাহিকাঃ
- শিরা: CO2 সমৃদ্ধ রক্ত দেহের বিভিন্ন অঙ্গ থেকে হৃদপিন্ড এ বয়ে নিয়ে আসে।ব্যতিক্রম পালমোনারি শিরা।
- কৈশিক জালিকা: রক্ত ও কলারসের মধ্যে ব্যাপন প্রক্রিয়ায়য় খাদ্যসার,O2,CO2,রেচন দ্রব্য ইত্যাদি আদান প্রদান করে।
- ধমনি: O2 সমৃদ্ধ রক্ত হৃদপিন্ড থেকে সারা দেহে পরিবহন করে।ব্যতিক্রম পালমোনারি ধমনি।
রক্তচাপঃ
- সিস্টোলিক চাপ-120 mmHg.
- ডায়াস্টোলিক চাপ-80 mmHg.
- নাড়ী চাপ-40 mmHg.
রক্তচাপ নিয়ন্ত্রণঃ
- উচ্চচাপ ব্যারোরিসিপ্টর।
- নিম্নচাপ ব্যারোরিসিপ্টর।
হৃদপিন্ডঃ লালচে-খয়েরী বর্ণের হৃদপিন্ডটি ত্রিকোণাকার মোচার মত।
আকার-আকৃতি:
- ত্রিকোণাকার,মোচার মত।
- ঊর্ধ্বাংশ চওড়া, বেস(base) বলে।
- নিম্মাংশ সরু, এপেক্স(apex) বলে।
- দৈর্ঘ্য 12 cm, প্রস্থ 9 cm.
অবস্থান:বক্ষ গহব্বরের মধ্য মিডিয়াস্টিনাম অঞ্চলের একটু বাম দিকে ডায়াফ্রামের উপরে ২ ফুসফুসের মধ্যস্থলে সামান্য হেলানো ভাবে ৫ম পাঁজরের ফাঁকে অবস্থিত।
আবরণ:
- প্যারাইটাল(বাহিরের স্তর)।
- ভিসেরাল(ভিতরের স্তর)।
তন্তুময় আবরণীকে 'ফাইব্রাস পেরিকার্ডিয়াম' বলে।
২ স্তরের মাঝের তরল পদার্থকে 'পেরিকার্ডিয়াল ফ্লুইড' বলে।
পেরিকার্ডিয়াল ফ্লুইড হৃদপিন্ডকে তাপ,চাপ,ঘর্ষণজনিত আঘাত থেকে রক্ষা করে।
পেশিস্তর/প্রাচীর:
- এপিকার্ডিয়াম(Epicardium):বাহিরের স্তর,বিক্ষিপ্তভাবে চর্বি জমে থাকে।
- মায়োকার্ডিয়াম(Myocardium):পেশি দৃঢ় প্রকৃতির,হৃদপিন্ডর সংকচন প্রসারণে সক্রিয় ভূমিকা রাখে।
- এন্ডোকার্ডিয়াম(Endocardium):সবচেয়ে ভেতরের স্তর,হৃদপিন্ডকে বিভিন্ন প্রকোষ্ঠ এ বিভক্ত করে,কপাটিকাসমূহ ঢেকে রাখে
প্রকোষ্ঠ :
- ডান অলিন্দ (Right Atrium)
- বাম অলিন্দ(Left Atrium)
- ডান নিলয় (Right Ventricle)
- বাম নিলয় (Left Ventricle)
- অলিন্দের তুলনায় নিলয়ের প্রাচীর পুরু ও পেশিবহুল।
- ডান অলিন্দের CO2 যুক্ত রক্ত আসে।
- বাম অলিন্দে O2 যুক্ত রক্ত আসে।
- অলিন্দ রক্তকে শুধু নিলয়ে সঞ্চালিত করে।
- বাম নিলয়ের প্রাচীর ডান নিলয়ের প্রাচীরের থেকে প্রায় ৩গুণ পুরু থাকে।
- ডান নিলয় কেবলমাত্র ফুসফুসে রক্ত সঞ্চালিত করে।
- বাম নিলয় সারা দেহে রক্ত সঞ্চালিত করে।
কপাটিকা:
১.ট্রাইকাসপিড কপাটিকা→ ডান অলিন্দ ও ডান নিলয়ের সংযোগস্থলে।
২.বাইকাসপিড কপাটিকা/মাইট্রাল কপাটিকা→বাম অলিন্দ ও বাম নিলয়ের সংযোগস্থলে।
৩.পালমোনারি কপাটিকা→ ডান নিলয় ও পালমোনারি ধমনীর সংযোগস্থলে।
৪.অ্যাওর্টিক কপাটিকা→ বাম নিলয় ও অ্যাওর্টার সংযোগস্থলে।
৫.থিবেসিয়ান কপাটিকা→ করোনারী সাইনাস ও ডান অলিন্দ এর সংযোগস্থলে।
৬.ইউস্টেসিয়ান কপাটিকা→ইনফিরিয়র ভেনাকেভা ও ডান অলিন্দ এর সংযোগস্থলে।
সেমিলুনার কপাটিকা / অর্ধচন্দ্রাকার কপাটিকা→পালমোনারি ও অ্যাওর্টিক ধমনির শুরুতে।
সংযোগকারী কলা:
১.সাইনো অ্যাট্রিয়াল নোড(SAN)→primary pace maker.
২.অ্যাট্রিও-ভেন্ট্রিকুলার নোড(AVN)
৩.বান্ডল অব হিজ(Bundle of His)
৪.পারকিনজি তন্তু।
বাইকাসপিড ও ট্রাইকাসপিড কপাটিকা কে নিলয়ের প্রাচীরের প্যাপিলারী পেশীর সাথে যুক্ত রাখে কর্ডি টেন্ডিনি।
Heart Sound:
১.লাব(Lub)→অলিন্দ-নিলয় কপাটিকা বন্ধের সময়।
২.ডাব(Dub)→সেমিলুনার কপাটিকা বন্ধের সময়।
হৃৎচক্র:
১.অলিন্দের ডায়াস্টোল=0.7 sec.
২.অলিন্দের সিস্টোল=0.1 sec.
৩.নিলয়ের সিস্টোল=0.3 sec.
৪.নিলয়ের ডায়াস্টোল=0.5 sec.
- সংকোচন কে সিস্টোল এবং প্রসারণ কে ডায়াস্টোল বলে।
- অলিন্দের 0.1sec + 0.7sec= 0.8 sec. এবং নিলয়ের 0.3 sec + 0.5 sec= 0.8 sec.একে কার্ডিয়াক চক্র বলে
- হৃৎস্পন্দন মিনিটে ৭৫বার গড়ে।
- SA nod মিনিটে ৭২বার।
- AV nod মিনিটে ৫০বার।
- bundle of His মিনিটে ৩৬বার।
- পারকিনজি তন্ত ৩০-৩৫বার।
রক্ত সংবহন পদ্ধতিঃ
1)সিস্টেমিক সংবহন : বামনিলয়→মহাধমনী→অঙ্গ→মহাশিরা→ডান অলিন্দ→ডান নিলয়
2)পালমোনারি সংবহন :
ডাননিলয়→পালমোনারী ধমনী→ফুসফুস→পালমোনারী শিরা→বামঅলিন্দ→বামনিলয়
3)করোনারী সংবহন :
হৃৎপিন্ডের প্রাচীরের রক্ত সংবহন।
4)পোর্টাল সংবহন।
হৃৎরোগঃ
১.অ্যানজাইনা(হৃৎশূল)।
২.হার্ট অ্যাটাক(মায়োকার্ডিয়াল ইনফার্কশন)।
৩.হার্ট ফেইলিউর।